刊·见 | 遥感SCI期刊,Geocarto International带您俯瞰地球
本期刊·见栏目,为您介绍遥感领域期刊Geocarto International,期刊致力于为遥感、地理信息系统、地球科学和环境科学领域的学者及业界提供最新研究成果。
Geocarto International 收录文章的范围包括:
- 有关遥感的新发展、新型技术应用相关的研究性论文、研究成果、创新性的项目及报告
- 遥感、地理信息系统以及相关领域的研究成果
- 新型GIS软件或硬件的评估与评价
该期刊已被SCIE,Scopus,EBSCO,PubMed,CAS,GEOBASE等国际知名数据库收录。
- 除了对期刊详尽的介绍外,我们还向您介绍刊内近三年高被引文章,以及近一年内高阅读量文章:
- 用于绘制洪水和侵蚀易发性地图的 GLM、FDA、MARS 和 RF 集合模型:子流域优先评估
- 从高分辨率航空图像构建语义分割的深度卷积 Segnet 和 Unet 网络的集合架构
- 评估印度一级城市的城市环境质量(UEQ):基于 RS-GIS 的探索性空间分析
影响因子
根据JCR显示,Geocarto International 的:
- 2022 影响因子:3.8
学科排名:
- 环境科学领域排名119/275
- 多学科地球科学领域排名60/202
- 成像科学与摄影技术领域排名12/28
- 遥感领域排名20/34
CiteScore
根据Scopus显示, Geocarto International 的
- CiteScore(2022)为4.3
- CiteScoreTracker(2023)为5.8
学科排名:
- 在社会科学:地理、规划与发展领域排名178/779
- 在环境科学:水科学与技术领域排名93/248
编辑团队
Geocarto International 的主编由Kamlesh Lulla(美国国家航空航天局/约翰逊航天中心)、M. Duane Nellis(俄亥俄大学名誉主席)和Bradley Rundquist(北达科他大学地理系)共同担任。此外,编辑团队中来自中国的是任职于中国地质大学(武汉)的窦杰教授。
主编介绍
Kamlesh Lulla

Kamlesh Lulla博士,高级科学家。任职于美国国家航空航天局(NASA),曾在航天飞机计划和国际空间站计划中担任地球观测和遥感高级(首席)科学职务。
M. Duane Nellis

M. Duane Nellis是俄亥俄大学的名誉校长兼董事会成员。2023年被任命为美国地理学家协会研究员,这一终身成就奖是对他在地理学领域(尤其是遥感技术)的专业知识以及在高等教育领域的领导力的认可。
Bradley Rundquist

Bradley Rundquist教授为北达科他大学地理系系主任,他的研究领域为环境遥感、数字图像处理、地理信息系统、生物地理学、自然地理学。
编委团队中国成员
窦杰

窦杰教授目前就职于中国地质大学(武汉),主要从事地质灾害人工智能大数据及智慧风险管控,数值模拟和遥感与GIS在降雨-水库-地震-人工诱发的地质灾害相关的预测预报研究工作。
作者分布
根据JCR显示,近三年在Geocarto International 发文的国家中排名前三位的是:
- 印度
- 中国
- 伊朗
近三年,在Geocarto International 发文的全球高校和科研机构中,发文数量排名前三位的是:
- 印度理工学院
- 印度航天局
- 中国科学院
近三年内高被引文章

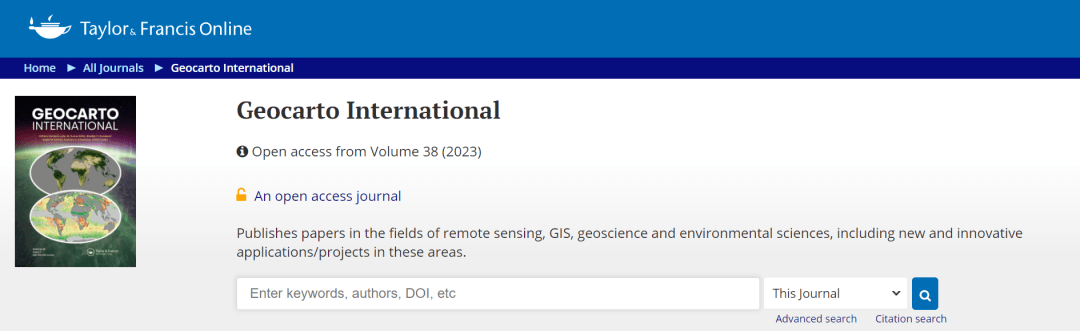
用于绘制洪水和侵蚀易发性地图的 GLM、FDA、MARS 和 RF 集合模型:子流域优先评估
作者:Amirhosein Mosavi et al.
 Flowchart steps to conduct research.
Flowchart steps to conduct research.
文章摘要:
The mountainous watersheds are increasingly challenged with extreme erosions and devastating floods due to climate change and human interventions. Hazard mapping is essential for local policymaking for prevention, planning the mitigation actions, and also adaptation to extremes. This study proposes novel predictive models for susceptibility mapping for flood and erosion. Furthermore, this study elaborates on prioritizing the existing sub-basins in terms of erosion and flood susceptibility. A comparative analysis of generalized linear model (GLM), flexible discriminate analyses (FDA), multivariate adaptive regression spline (MARS), random forest (RF), and their ensemble is performed to ensure highest predictive performance. Furthermore, the priority of the sub-basins in terms of sensitivity to erosion and flood was determined based on the best model. The results showed that the GLM, FDA, MARS, RF, and ensemble models had an area under curve (AUC) 0.91, 0.92, 0.89, 0.93 and 0.94, respectively, in modeling the flood susceptibility. Also, the GLM, FDA, MARS, RF, and ensemble models had an AUC of 0.93, 0.92, 0.89, 0.96, and 0.97, respectively, in determining erosion susceptibility. Priority assessment based on the best model, the ensemble approach, indicated that the sub-basins SW3 and SW5 were found to have high sensitivity to the flood and soil erosion, respectively.

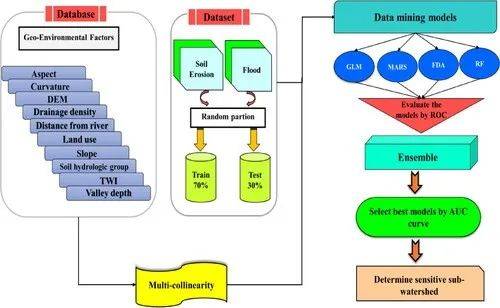
从高分辨率航空图像构建语义分割的深度卷积 Segnet 和 Unet 网络的集合架构
作者:Abolfazl Abdollahi et al.
 Overall methodology of the proposed Seg–Unet model for build
Overall methodology of the proposed Seg–Unet model for build
Overall methodology of the proposed Seg–Unet model for building extraction.
文章摘要:
Building objects is one of the principal features that are essential for updating the geospatial database. Extracting building features from high-resolution imagery automatically and accurately is challenging because of the existence of some obstacles in these images, such as shadows, trees, and cars. Although deep learning approaches have shown significant improvements in the results of image segmentation in recent years, most deep neural networks still cannot achieve highly accurate results with correct segmentation map when processing high-resolution remote sensing images. Therefore, we implemented a new deep neural network named Seg–Unet method, which is a composition of Segnet and Unet techniques, to exploit building objects from high-resolution aerial imagery. Results obtained 92.73% accuracy carried on the Massachusetts building dataset. The proposed technique improved the performance to 0.44%, 1.17%, and 0.14% compared with fully convolutional neural network (FCN), Segnet, and Unet methods, respectively. Results also confirmed the superiority of the proposed method in building extraction.
近一年内高阅读量文章

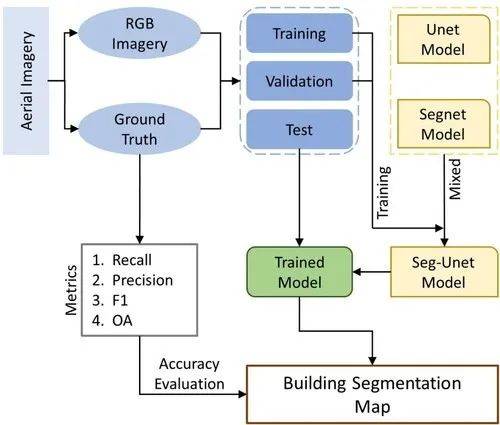
评估印度一级城市的城市环境质量(UEQ):基于 RS-GIS 的探索性空间分析
作者:Subham Roy et al.
 Methodological flow chart adopted for the present study.
Methodological flow chart adopted for the present study.
文章摘要:
Urban environmental quality consisting of ecological, physical, and socio-economic components, often deteriorates due to rapid urbanization. Therefore, using Remote sensing and GIS environment, a composite measure is applied to quantify the spatial heterogeneity of urban environmental quality for the Class-1 Indian city (Siliguri). In this study, the Urban Environmental Quality Index was constructed using 15 indicators and three interconnected dimensions (eco-environment, landscape and built-up, and socio-economy). The three domains and Urban Environmental Quality Index were computed utilizing Principal Component Analysis with average aggregation techniques. Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis includes Moran’s I and Local indicator of spatial auto-correlation, were used to leverage the information of spatial clusters, spatial heterogeneity, and outliers based on the Urban Environmental Quality Index. The results show that Siliguri’s northern, north-western, and southern parts experience good environmental quality. The effectiveness of the employed model was checked using R2 (0.832), providing a good fit for the model. Moreover, the spatial pattern of urban environmental quality and the constructed domains (except socio-economy) revealed that the Low-Low values were predominantly clustered in the city centre, while High-High patterns are concentrated towards the periphery. Also, the value of Moran’s I indicated the existence of spatial autocorrelation and non-randomness pattern in Siliguri City. The results obtained from the analysis indicate spatial heterogeneity and spatial differentiation across the study area. The study’s outcome is relevant for urban planning, frequent monitoring of urban environmental quality, urban governance, and the well-being of urban inhabitants for a sustainable urban space.
文章出版费(APC)
请访问期刊主页或使用Taylor & Francis Open Access APC Cost Finder查找适用于作者所在国家及不同文章类型的费用情况。若您所在的机构或相关资助者与Taylor & Francis签有开放获取出版协议,您可能有资格获得APC支持,请访问我们的作者服务网站以了解更多!
Taylor & Francis现在开通APC便捷支付功能,可以一键通过微信、支付宝和银联使用人民币便捷付款。
为帮助更多科研人员选择更加合适的期刊,Taylor & Francis推出专栏——刊·见,该专栏致力于为读者和广大科研人员带来Taylor & Francis旗下期刊的详细解读,从期刊的基本情况、编委阵容、社会影响力到审稿速度、高被引文章等实用信息,专栏将为您带来最详细的介绍,让您更加全面地了解Taylor & Francis旗下优秀的国际期刊,帮助更多中国卓越科研成果顺利在国际期刊上发表。
以上内容可能更新,请以期刊官网主页为准。
点击来这里👉http://985.so/2c35y,查看期刊最新数据和投稿详情!
